How to Improve Email Deliverability (2026 Guide)
10 January 2026

Short answer: Email deliverability improves when you authenticate your domain (SPF, DKIM, DMARC), maintain clean email lists, and build sender reputation through consistent engagement. Focus on authentication first—Gmail and Yahoo now require it for bulk senders. A good email deliverability rate is 95% or higher; below 90% signals serious problems requiring immediate action (Source).
Table of Contents
- What Is Email Deliverability?
- Why Is Email Deliverability Important?
- What Affects Email Deliverability?
- What Is a Good Email Deliverability Rate?
- How to Improve Email Deliverability: 7 Strategies That Work
- How to Test and Measure Email Deliverability
- How to Fix Email Deliverability Issues
- B2B Email Deliverability: What’s Different
- When to Use Email Deliverability Services
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How long does it take to improve email deliverability?
- Can I recover from a blacklisted domain?
- Does email size affect deliverability?
- How often should I clean my email list?
- What’s the difference between email delivery and email deliverability?
- How do spam traps affect deliverability?
- Should I use a dedicated IP or shared IP?
- Why are my emails going to spam suddenly?
- How do I check if my domain is blacklisted?
- Do engagement rates affect deliverability?
Key Takeaways:
- Authentication is mandatory: Configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC before sending any campaigns
- List hygiene drives reputation: Remove bounces and inactive subscribers monthly
- Gmail/Yahoo 2025 rules changed everything: One-click unsubscribe and <0.3% spam complaints are now required
- Warm up new domains: Start with 50-100 emails/day, scale over 4-6 weeks
- Monitor constantly: Use Google Postmaster Tools and seed testing to catch issues early
This guide covers what affects email deliverability, how to test and measure it, and the exact steps to fix deliverability issues—whether you’re troubleshooting a sudden drop or building reputation from scratch.
What Is Email Deliverability?
Email deliverability is the rate at which your emails reach subscribers’ inboxes instead of spam folders or getting blocked entirely. It measures whether mailbox providers (Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo) trust your sending reputation enough to let your messages through.
This is different from delivery rate, which only tracks whether an email was accepted by the receiving server—not where it landed.
| Metric | What It Measures | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Rate | Emails accepted by server (not bounced) | 98% delivered = 2% hard bounced |
| Deliverability Rate | Emails that reached the inbox | 85% inbox = 15% went to spam or promotions |
| Inbox Placement Rate | Emails in primary inbox specifically | 72% primary inbox vs tabs/folders |
You can have 99% delivery rate and terrible deliverability. The server accepted your email—then routed it straight to spam. That’s why deliverability is the metric that actually matters for campaign performance.
Why Is Email Deliverability Important?
Email deliverability determines whether your campaigns generate revenue or disappear into spam folders. A 10% drop in deliverability means 10% of your audience never sees your message—and that compounds across every campaign you send.
The math is brutal:
- 100,000 subscribers at 95% deliverability = 95,000 reach
- 100,000 subscribers at 80% deliverability = 80,000 reach
- That’s 15,000 lost contacts per send—without a single unsubscribe
Deliverability also affects every downstream metric. Open rates, click rates, and conversions all depend on emails actually reaching the inbox. If you’re troubleshooting “low engagement,” the problem often starts with deliverability, not subject lines.
Sender reputation compounds over time. Mailbox providers track your sending history. Good deliverability builds trust, which improves future deliverability. Poor deliverability triggers spam filtering, which tanks engagement, which destroys reputation further. The spiral moves fast in both directions.
For B2B senders, the stakes are higher. Corporate spam filters (Barracuda, Proofpoint, Mimecast) are more aggressive than consumer filters. One blacklisting can cut off access to entire company domains.
What Affects Email Deliverability?
Email deliverability depends on four factors: authentication, sender reputation, content quality, and subscriber engagement. Mailbox providers weigh all four when deciding whether to inbox, spam, or block your emails.
| Factor | What It Includes | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | SPF, DKIM, DMARC configuration | Required (pass/fail gate) |
| Sender Reputation | IP reputation, domain reputation, complaint history | High (primary scoring factor) |
| Content Quality | Spam triggers, link hygiene, text-to-image ratio | Medium (can trigger filters) |
| Subscriber Engagement | Opens, clicks, replies, spam complaints | High (signals legitimacy) |
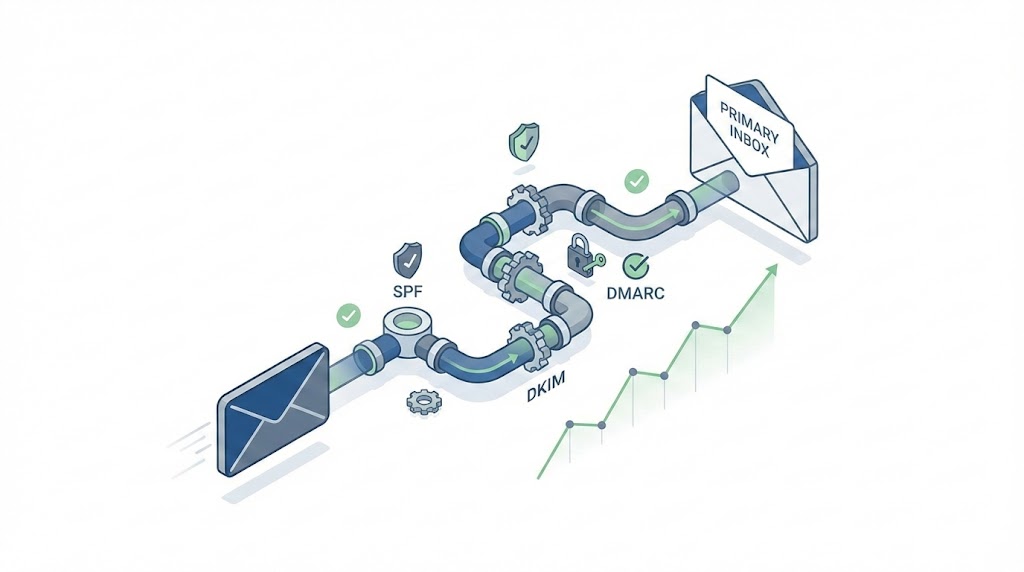
Authentication is a gate, not a score. Without proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records, Gmail and Yahoo will reject or spam your emails regardless of how good everything else is. Since February 2024, this is non-negotiable for bulk senders (Source).
Sender reputation is the primary score. Mailbox providers track your sending history across millions of data points. High complaint rates, spam trap hits, or inconsistent sending patterns damage reputation quickly. Rebuilding takes months.
Content triggers are secondary but dangerous. Certain phrases, excessive links, URL shorteners, and image-heavy emails can trip spam filters even with good reputation.
Engagement signals legitimacy. When subscribers open, click, and reply to your emails, mailbox providers learn your messages are wanted. Low engagement tells them the opposite—and they act accordingly.
What Is a Good Email Deliverability Rate?
A good email deliverability rate is 95% or higher. This means 95 out of 100 emails land in the inbox—not spam, not promotions tabs, not blocked. Below 90% indicates serious issues requiring immediate attention (Source).
| Deliverability Rate | Status | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| 95%+ | Healthy | Maintain current practices, monitor monthly |
| 90-95% | Needs Improvement | Audit authentication, clean list, check reputation |
| 80-90% | Problem | Immediate troubleshooting, pause non-essential sends |
| Below 80% | Critical | Stop sending, full audit, possible domain/IP change |
Industry benchmarks vary. SaaS and B2B companies typically see 92-97% deliverability. E-commerce with large promotional lists often runs 88-94%. Financial services and healthcare face stricter filtering, so 90%+ is considered strong.
Don’t confuse deliverability with delivery rate. Most ESPs report delivery rate (emails accepted by servers), not inbox placement. You can show 98% “delivered” while half your emails sit in spam. True deliverability requires inbox placement testing with seed lists.
Track the trend, not just the number. A stable 93% is healthier than a 96% that dropped from 99%. Sudden drops signal reputation damage, blacklisting, or authentication failures—investigate immediately even if you’re still above 90%.
How to Improve Email Deliverability: 7 Strategies That Work
These seven strategies address the root causes of deliverability problems. Start with authentication—it’s the foundation everything else depends on. Then work through reputation, list hygiene, and engagement in order.
1. Set Up Email Authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
Email authentication proves you are who you say you are. Without it, mailbox providers assume you’re a spammer or phisher. Since February 2024, Gmail and Yahoo reject or spam emails from unauthenticated bulk senders.
| Protocol | What It Does | Setup Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| SPF (Sender Policy Framework) | Lists which servers can send email for your domain | Easy (one DNS TXT record) |
| DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) | Adds cryptographic signature to verify email wasn’t altered | Medium (requires key generation) |
| DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication) | Tells receivers what to do when SPF/DKIM fail | Easy (one DNS TXT record) |
How to set up authentication:
- Access your domain’s DNS settings (via registrar or hosting provider)
- Add SPF record:
v=spf1 include:_spf.youresp.com ~all(replace with your ESP’s include) - Generate DKIM keys in your email service provider dashboard
- Add DKIM TXT record to DNS with the public key
- Create DMARC record:
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@yourdomain.com - Monitor DMARC reports for 2-4 weeks
- Gradually tighten DMARC policy:
p=none→p=quarantine→p=reject
Common mistakes: Using multiple SPF records (only one allowed), not including all sending sources in SPF, setting DMARC to p=reject before monitoring. Any of these will tank deliverability.
2. Meet Gmail and Yahoo 2025 Bulk Sender Requirements
Gmail and Yahoo implemented strict requirements for bulk senders (5,000+ emails/day) starting February 2024. These rules apply to everyone now—enforcement has only gotten stricter in 2025 (Source).
| Requirement | Threshold | What Happens If You Fail |
|---|---|---|
| Email Authentication | SPF, DKIM, and DMARC all required | Emails rejected or sent to spam |
| Spam Complaint Rate | Below 0.3% (target under 0.1%) | Throttling, then blocking |
| One-Click Unsubscribe | List-Unsubscribe header required | Emails flagged as non-compliant |
| Valid Forward/Reverse DNS | PTR records must match sending IP | Emails rejected at server level |
| TLS Connection | Emails must be sent over TLS encryption | Emails rejected |
The 0.3% spam complaint threshold is brutal. That’s 3 complaints per 1,000 emails. One bad campaign to a stale list can exceed this instantly. Google recommends staying under 0.1% for safety margin. (Source)
One-click unsubscribe is non-negotiable. Your emails must include a List-Unsubscribe header that works with one click—no confirmation pages, no login required. Most modern ESPs handle this automatically, but verify yours does.
3. Build and Protect Your Sender Reputation
Sender reputation is a score mailbox providers assign to your IP address and domain based on sending history. High reputation means inbox placement. Low reputation means spam folder or outright blocking.
Two types of reputation matter:
- IP reputation: Tied to the server IP address sending your emails. Shared IPs pool reputation across all senders; dedicated IPs give you full control.
- Domain reputation: Tied to your sending domain. Follows you even if you change IPs or ESPs. Increasingly weighted more heavily than IP reputation.
When to use dedicated vs. shared IP:
| Sending Volume | Recommended | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Under 50,000/month | Shared IP | Not enough volume to build dedicated IP reputation |
| 50,000-100,000/month | Either (depends on consistency) | Dedicated works if you send consistently |
| Over 100,000/month | Dedicated IP | Full control, isolation from other senders |
Reputation killers to avoid:
- Spam traps: Email addresses that exist only to catch spammers. Pristine traps were never real addresses. Recycled traps are abandoned addresses reactivated as traps. Hitting either destroys reputation.
- High complaint rates: Every “mark as spam” click damages your score. Stay under 0.1%.
- Inconsistent sending: Sending 10,000 emails one week, zero the next, then 50,000 looks like spammer behavior. Maintain consistent volume.
- Purchased lists: Guaranteed spam traps, complaints, and bounces. Never worth it.
4. Clean Your Email List Regularly
List hygiene directly impacts deliverability. Invalid addresses cause bounces. Inactive subscribers kill engagement metrics. Both signal to mailbox providers that you don’t manage your list responsibly.
What to remove:
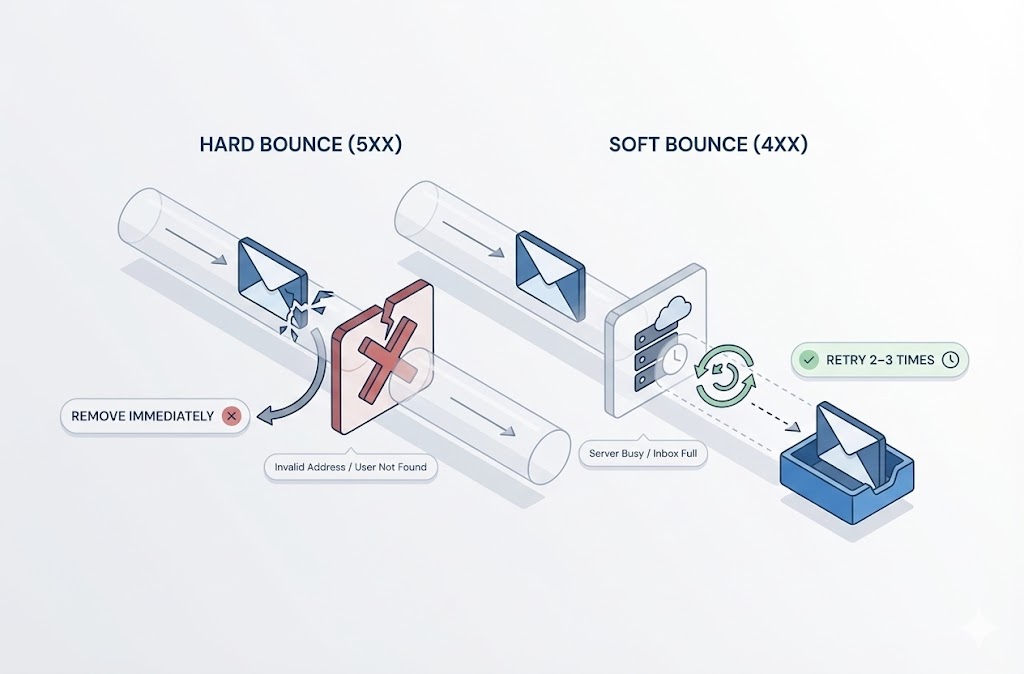
- Hard bounces: Remove immediately after first bounce. These addresses don’t exist.
- Soft bounces: Remove after 3-5 consecutive soft bounces. Temporary issues became permanent.
- Spam complainers: Remove anyone who complained. Sending again guarantees another complaint.
- Inactive subscribers: No opens or clicks in 6-12 months. Re-engage or remove.
How to clean your list:
- Export your full email list from your ESP
- Run through an email verification service to identify invalid, risky, and catch-all addresses
- Remove or quarantine addresses flagged as invalid, spam traps, or disposable
- Segment unverified/risky addresses for slower sending or exclusion
- Re-import cleaned list
- Set up automated hygiene: remove hard bounces instantly, flag soft bounces, sunset inactive subscribers
Use double opt-in for new subscribers. Double opt-in requires subscribers to confirm their email address before being added to your list. This eliminates typos, fake signups, and bot registrations. Your list grows slower but stays cleaner.
Cleaning frequency: Monthly for active senders, quarterly minimum for everyone. Clean before any major campaign to a full list.
5. Warm Up New Domains and IPs
New domains and IP addresses have no sending reputation. Mailbox providers treat unknown senders with suspicion. Warmup builds trust gradually by starting with low volume and scaling over time.
Why warmup matters: Sending 50,000 emails from a brand-new domain looks like a spammer who just registered a throwaway domain. Mailbox providers will throttle or block you. Warmup proves you’re a legitimate sender with engaged recipients.
Warmup schedule for new domains/IPs:
- Week 1: 50-100 emails/day to your most engaged subscribers only
- Week 2: 200-500 emails/day, still prioritizing engaged contacts
- Week 3: 500-1,000 emails/day, expand to moderately engaged
- Week 4: 1,000-5,000 emails/day
- Week 5-6: 5,000-10,000 emails/day
- Week 6+: Scale to full volume, monitoring metrics closely
Warmup rules:
- Send only to confirmed, engaged subscribers during warmup
- Maintain consistent daily sending (don’t skip days)
- Monitor bounce rates, spam complaints, and inbox placement at each stage
- If metrics dip, pause and stabilize before increasing volume
- Prioritize Gmail and Outlook recipients—they’re strictest during warmup
Signs warmup is working: Inbox placement above 90%, bounce rate under 2%, spam complaints under 0.1%, steady or improving open rates as you scale.
Signs warmup is failing: Rising bounce rates, dropping open rates, emails landing in spam, throttling messages from mailbox providers. Stop scaling immediately, investigate, fix, then resume.
6. Optimize Email Content for Inbox Placement
Content filters scan your emails for spam signals. Even with good authentication and reputation, certain content patterns trigger filtering. Optimize your emails to avoid these traps.
Subject line best practices:
- Avoid all caps: “FREE OFFER!!!” triggers filters
- Skip excessive punctuation: “Act now!!!” looks spammy
- Don’t use spam trigger phrases: “100% free,” “Act now,” “Limited time,” “Click here”
- Keep under 50 characters for mobile display
- Personalization helps: Using the recipient’s name signals legitimacy
Email body optimization:
- Text-to-image ratio: Aim for 60% text, 40% images minimum. Image-only emails get filtered.
- Alt text on images: Spam filters can’t read images. Alt text provides context and helps deliverability.
- Link hygiene: Avoid URL shorteners (bit.ly, etc.)—they’re heavily abused by spammers. Use full URLs from reputable domains.
- Limit total links: Excessive links (10+) look like phishing. Keep it under 5 when possible.
- Avoid attachments: Attachments trigger security filters. Host files and link to them instead.
HTML structure matters:
- Use clean, well-formatted HTML (broken code triggers filters)
- Include a plain-text version of every email
- Don’t hide text (white text on white background is a spam signal)
- Avoid embedded JavaScript (auto-blocked by most clients)
7. Improve Engagement Signals
Mailbox providers track how recipients interact with your emails. High engagement signals legitimacy and earns inbox placement. Low engagement signals unwanted email and triggers spam filtering.
Engagement signals that matter:
- Opens: Recipient opened the email (indicates interest)
- Clicks: Recipient clicked a link (strong positive signal)
- Replies: Recipient replied to the email (strongest positive signal)
- Spam complaints: Recipient marked as spam (strongest negative signal)
- Deletes without reading: Recipient deleted without opening (mild negative signal)
How to improve engagement:
- Segment by engagement level: Create segments for highly engaged (opened in last 30 days), moderately engaged (opened in 30-90 days), and inactive (no opens in 90+ days). Send your most important campaigns to engaged segments first.
- Personalize beyond first name: Use behavioral data—past purchases, content interests, browsing history—to send relevant content. Relevant emails get opened.
- Optimize send times: Test different days and times for your audience. B2B typically performs better Tuesday-Thursday mornings. B2C varies widely. Let data guide you.
- Re-engage or sunset inactive subscribers: Send a re-engagement campaign to inactive subscribers. Those who don’t respond within 2-3 attempts should be removed. Keeping them hurts deliverability.
- Ask for replies: Replies are the strongest engagement signal. Ask a question, request feedback, or invite responses. Even a small percentage of replies significantly boosts sender reputation.
- Make unsubscribing easy: A visible, one-click unsubscribe reduces spam complaints. People who unsubscribe instead of complaining protect your reputation.
How to Test and Measure Email Deliverability
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Testing email deliverability requires tracking the right metrics, using the right tools, and understanding what the numbers actually mean.
Key Metrics to Track
| Metric | What It Tells You | Target Range |
|---|---|---|
| Inbox Placement Rate | Percentage of emails landing in inbox (not spam) | 95%+ healthy, below 90% problematic |
| Bounce Rate | Percentage of emails rejected by servers | Under 2% acceptable, under 0.5% ideal |
| Spam Complaint Rate | Percentage of recipients marking email as spam | Under 0.1% ideal, above 0.3% critical |
| Open Rate | Engagement indicator (indirect deliverability signal) | 15-25% typical, varies by industry |
| Unsubscribe Rate | List health indicator | Under 0.5% per campaign |
Bounce rate breakdown—know the difference:
- Hard bounce: Permanent failure. Address doesn’t exist, domain invalid, or recipient server permanently rejected. Remove immediately.
- Soft bounce: Temporary failure. Mailbox full, server down, or message too large. Retry automatically. Remove after 3-5 consecutive failures.
A sudden spike in hard bounces indicates list quality issues—you’re sending to outdated or purchased addresses. A spike in soft bounces might indicate reputation problems causing temporary blocks.
Tools for Testing Deliverability
Google Postmaster Tools (Free)
Essential for anyone sending to Gmail recipients. Shows your domain reputation, spam rate, authentication status, and delivery errors. Setup takes 5 minutes—just verify your domain.
What to monitor:
- Domain reputation (High/Medium/Low/Bad)
- IP reputation
- Spam rate (keep under 0.1%)
- Authentication success rate (should be 100%)
Seed List Testing
Seed testing sends your email to a panel of test addresses across major mailbox providers (Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, corporate). You see exactly where emails land—inbox, spam, promotions, or blocked.
Tools that offer seed testing:
- GlockApps
- Mail-Tester
- Inbox Ally
- Everest (Validity)
Run seed tests before major campaigns and whenever you suspect deliverability issues.
Blocklist Monitoring
Blocklists (Spamhaus, Barracuda, SpamCop) track IPs and domains with spam complaints. Getting listed tanks deliverability instantly. Monitor your status regularly.
Free blocklist checkers:
- MXToolbox
- MultiRBL
- Spamhaus lookup
If you’re listed, each blocklist has a removal process. Fix the underlying issue first—removal without fixing guarantees re-listing.
Email Authentication Checkers
Verify your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are configured correctly:
- MXToolbox SuperTool
- DMARC Analyzer
- Mail-Tester.com
Run these checks after any DNS changes and quarterly as routine maintenance.
How to Check Email Deliverability: Quick Audit
- Check Google Postmaster Tools for domain/IP reputation
- Run a blocklist check on your sending IP and domain
- Verify authentication with MXToolbox
- Send a seed test to check inbox placement across providers
- Review ESP dashboard for bounce and complaint rates
- Compare open rates to your historical baseline
If any step shows problems, investigate before sending your next campaign.
How to Fix Email Deliverability Issues
Fixing deliverability problems requires diagnosing the root cause first. Random fixes waste time and can make things worse. Use this systematic approach to identify what’s broken and fix it in the right order.
Diagnostic Flowchart
Start here → Check authentication
- SPF/DKIM/DMARC failing? → Fix DNS records first
- Authentication passing? → Check reputation
Check reputation
- Domain/IP reputation low? → Pause sending, investigate cause
- Reputation healthy? → Check list quality
Check list quality
- Bounce rate above 2%? → Clean list immediately
- Complaint rate above 0.1%? → Audit content and frequency
- List clean? → Check content
Check content
- Spam filter triggers present? → Rewrite content
- Content clean? → Check engagement
Check engagement
- Open rates dropping? → Segment and re-engage
- Engagement healthy? → Monitor and maintain
Common Causes and Fixes
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Emails going to spam (all providers) | Authentication failure or domain reputation | Verify SPF/DKIM/DMARC, check Postmaster Tools |
| Emails going to spam (Gmail only) | Gmail-specific reputation issue | Check Google Postmaster Tools, reduce Gmail volume temporarily |
| High bounce rate suddenly | List decay or bad data source | Verify list through email verification service, remove invalids |
| Blacklisted IP/domain | Spam trap hit or complaint spike | Request delisting, identify and remove bad addresses, pause sending |
| Low open rates across all campaigns | Inbox placement issues or list fatigue | Run seed test, segment by engagement, reduce frequency |
| Emails blocked by corporate filters | IP/domain reputation with Barracuda, Proofpoint, etc. | Check specific blocklists, request whitelisting, warm up slowly |
| Deliverability dropped after ESP migration | New IP without reputation | Proper warmup sequence, migrate engaged subscribers first |
| Inconsistent deliverability | Shared IP reputation fluctuation | Consider dedicated IP if volume supports it |
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Process
- Stop the bleeding: If deliverability crashed suddenly, pause non-essential campaigns. Continuing to send with low reputation makes it worse.
- Check authentication first: Use MXToolbox to verify SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Any failures here override everything else—fix before proceeding.
- Check blocklists: Run your sending IP and domain through MXToolbox blocklist check. If listed, start the delisting process immediately.
- Review Google Postmaster Tools: Check domain reputation, spam rate, and authentication status. This shows exactly how Gmail views you.
- Audit recent campaigns: Look for the campaign that triggered the drop. Check bounce rates, complaint rates, and engagement. Identify what changed.
- Clean your list: Run your entire list through email verification. Remove invalids, spam traps, and high-risk addresses. This is non-negotiable for recovery.
- Reduce volume and rebuild: Send only to your most engaged segment (opened in last 30 days) for 2-4 weeks. Rebuild reputation through positive engagement before scaling back up.
- Monitor daily during recovery: Watch metrics closely. Any setback means pausing and investigating again.
Using Monitoring Tools to Fix Issues
Email monitoring tools track deliverability metrics continuously and alert you to problems before they become critical. This addresses the question of how to fix email deliverability with monitoring—proactive detection prevents major reputation damage.
What monitoring tools catch:
- Blacklist additions (within hours, not days)
- Authentication failures after DNS changes
- Sudden reputation drops
- Inbox placement changes by provider
When monitoring matters most:
- After migrating ESPs or adding sending infrastructure
- When scaling volume significantly
- During and after warmup periods
- For high-volume senders (100k+/month)
Tools like Validity Everest, GlockApps, and 250ok provide continuous monitoring. For lower volume senders, weekly manual checks using free tools work—but set calendar reminders. Deliverability problems compound quickly when undetected.
How to Fix Low Email Deliverability Rates
If your deliverability rate is below 90%, treat it as urgent:
- Immediate: Pause all campaigns except to highly engaged subscribers
- Day 1-3: Complete full diagnostic (authentication, blocklists, reputation, list quality)
- Day 4-7: Fix identified issues, clean list, request any blocklist removals
- Week 2-4: Send only to engaged segments, monitor daily
- Week 5+: Gradually reintroduce segments as metrics stabilize
Recovery takes 4-8 weeks minimum for serious reputation damage. Rushing the process by scaling too fast will reset your progress.
B2B Email Deliverability: What’s Different
B2B email deliverability follows the same fundamentals as B2C, but corporate email environments add complexity. Understanding these differences is essential for improving B2B email campaign deliverability.
Corporate Spam Filters Are More Aggressive
Consumer mailbox providers (Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook.com) use reputation-based filtering. Corporate email systems add dedicated security gateways that apply stricter rules.
| Filter Type | Common Providers | What They Block |
|---|---|---|
| Secure Email Gateways | Proofpoint, Mimecast, Barracuda | Unknown senders, suspicious links, attachment types |
| Microsoft 365 Defender | Built into Office 365 | Phishing patterns, impersonation attempts, bulk mail |
| Google Workspace Filters | Built into Google Workspace | Similar to Gmail but with admin-level controls |
| On-Premise Filters | Exchange, custom solutions | Varies by IT policy—often very restrictive |
What this means for you: An email that reaches Gmail inboxes might get blocked entirely by Proofpoint. B2B senders need to monitor deliverability by recipient domain type, not just overall metrics.
Lower Volume Makes Reputation Harder to Build
B2B email lists are smaller than B2C. A SaaS company might have 10,000 prospects; an e-commerce brand has 500,000. Lower volume creates specific challenges:
- Slower warmup: Less data for mailbox providers to evaluate means longer reputation building
- Higher impact per complaint: One spam complaint in 1,000 emails is 0.1%. One complaint in 100 emails is 1%—immediate reputation damage.
- Inconsistent sending patterns: B2B campaigns often follow sales cycles, not consistent schedules. Irregular sending looks suspicious.
How to adapt:
- Maintain minimum weekly sending even during slow periods
- Prioritize engagement quality over list size
- Consider shared IP pools designed for low-volume B2B senders
Decision-Maker Targeting Adds Risk
B2B campaigns target specific roles: CEOs, VPs, Directors. These addresses are often:
- Heavily guarded: Executive assistants screen email, IT applies extra filtering
- Less engaged: Senior decision-makers have overflowing inboxes
- More likely to complain: Unsolicited emails to executives generate complaints faster
Mitigation strategies:
- Warm up executive-level contacts through other channels first (LinkedIn, referrals)
- Lead with value, not sales pitch—executives delete promotional emails instantly
- Keep initial outreach short and personalized—long emails get filtered or ignored
BIMI for B2B Brand Recognition
BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification) displays your logo next to emails in supported inboxes. For B2B, this builds trust and recognition with prospects who receive dozens of vendor emails daily.
BIMI requirements:
- DMARC policy at
p=quarantineorp=reject - Verified Mark Certificate (VMC) from approved certificate authority
- SVG logo file meeting technical specifications
BIMI adoption is still growing, but early adopters gain visibility advantage—especially in crowded B2B markets where standing out in the inbox matters.
B2B-Specific Deliverability Checklist
- Monitor deliverability by corporate vs. consumer domains separately
- Check Barracuda and Proofpoint blocklists specifically (not just Spamhaus)
- Maintain consistent sending schedule even with lower volume
- Warm up slower—extend standard warmup timeline by 50%
- Personalize beyond mail merge—generic templates trigger corporate filters
- Consider BIMI implementation for brand recognition
- Test deliverability to sample corporate domains before major campaigns
When to Use Email Deliverability Services
Email deliverability services range from verification tools to full-service consulting. Knowing when to handle deliverability in-house versus hiring help saves money and accelerates recovery.
Benefits of Email Deliverability Services
Professional deliverability services provide expertise and tools most marketing teams don’t have internally:
- Diagnostic capabilities: Access to seed testing networks, blocklist monitoring, and reputation tracking across providers
- Faster troubleshooting: Experienced consultants identify root causes in hours, not weeks
- Relationship with ISPs: Established providers have contacts at major mailbox providers for escalations
- Ongoing monitoring: Continuous tracking catches problems before they become crises
- Strategic guidance: Advice on infrastructure, warmup, and sending practices tailored to your situation
DIY vs. Managed Services Decision Framework
| Situation | DIY Appropriate | Professional Help Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Deliverability rate | Above 90%, stable | Below 90% or dropping fast |
| Technical expertise | Team understands DNS, authentication, ESP settings | No in-house email infrastructure knowledge |
| Volume | Under 100k/month | Over 500k/month or rapid scaling |
| Problem complexity | Single issue (bounces OR reputation OR content) | Multiple simultaneous issues or unknown cause |
| Time to fix | Can wait 4-8 weeks for gradual improvement | Revenue-critical campaigns blocked now |
| Budget | Limited—need free/low-cost solutions | Can invest $1,000-10,000+ for expert help |
Types of Deliverability Services
Email Verification Services
Validate email addresses before sending. Removes invalid addresses, spam traps, and high-risk contacts. This is the lowest-cost, highest-impact first step for most deliverability problems.
Use case: List hygiene, reducing bounce rates, protecting sender reputation
Cost: $0.001-0.01 per email verified
Deliverability Monitoring Tools
Continuous tracking of inbox placement, blocklist status, and authentication. Alerts you to problems as they happen.
Use case: Ongoing prevention, early warning system, performance benchmarking
Cost: $50-500/month depending on volume and features
Deliverability Audits
One-time comprehensive review of your sending infrastructure, authentication, reputation, and practices. Delivers a report with specific fixes.
Use case: Diagnosing persistent problems, pre-launch infrastructure review, post-incident analysis
Cost: $500-5,000 depending on scope
Managed Deliverability Services
Ongoing expert management of your email deliverability. Includes monitoring, troubleshooting, ISP relations, and strategic guidance.
Use case: High-volume senders, companies without in-house expertise, critical email revenue dependency
Cost: $1,000-10,000+/month
Deliverability Consultants
Project-based expert help for specific problems or initiatives. Useful for migrations, warmup planning, or crisis recovery.
Use case: ESP migration, reputation recovery, scaling strategy
Cost: $150-400/hour or project-based
When to Start With Verification
For most deliverability problems, email verification is the right first step:
- It’s immediate: Results in minutes, not weeks
- It’s affordable: Verify 100,000 emails for under $500
- It addresses root causes: Invalid addresses cause bounces, which damage reputation, which kills deliverability
- It’s required anyway: No consultant or service can fix deliverability if you’re sending to bad addresses
If your bounce rate is above 2% or you haven’t verified your list in 6+ months, start here before investing in higher-cost services.
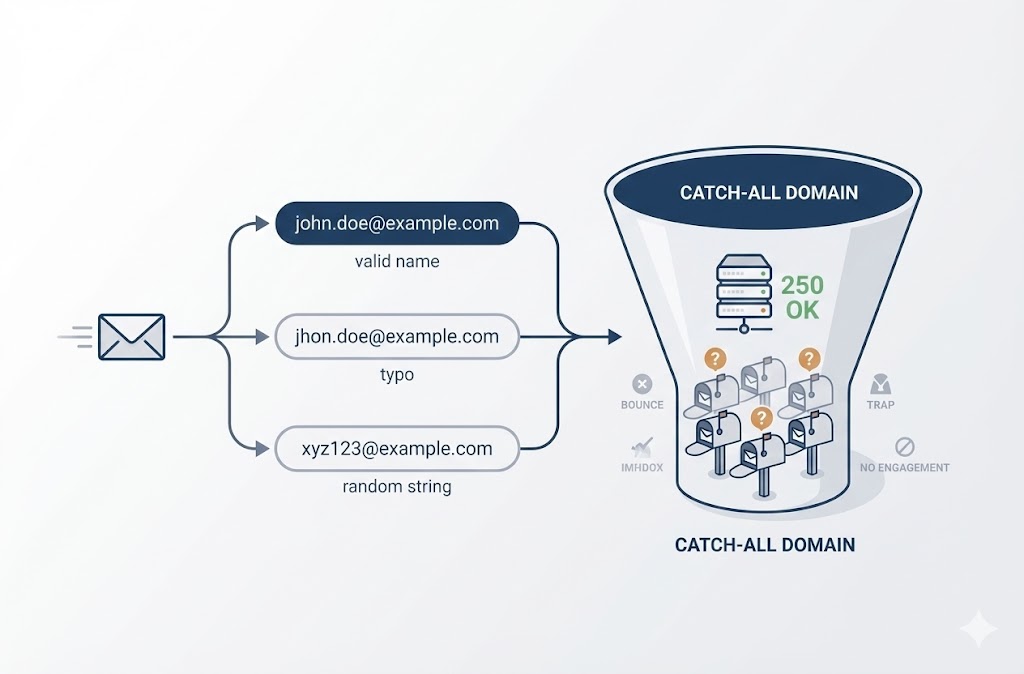
BoltRoute’s email verification identifies invalid addresses, spam traps, catch-all domains, and risky contacts before they damage your sender reputation. Clean lists are the foundation every other deliverability improvement depends on.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to improve email deliverability?
Minor issues (authentication fixes, list cleaning) show improvement within 1-2 weeks. Reputation recovery from serious damage takes 4-8 weeks minimum. Full recovery from blacklisting or major spam trap hits can take 3-6 months. Consistency matters more than speed—rushing the process by scaling too fast resets progress.
Can I recover from a blacklisted domain?
Yes, but it requires effort. First, identify why you were listed (spam traps, complaints, compromised sending). Fix the root cause completely. Then submit a delisting request to each blocklist—most have online forms. Some blocklists (Spamhaus, Barracuda) respond within 24-48 hours if your request is legitimate. Others take longer. If the underlying problem isn’t fixed, you’ll be relisted within days.
Does email size affect deliverability?
Indirectly. Emails over 100KB may load slowly or trigger soft bounces on recipients with full mailboxes. Image-heavy emails (large file sizes) often have poor text-to-image ratios, which triggers spam filters. Keep emails under 100KB total. Use hosted images instead of embedded ones. The content matters more than raw size.
How often should I clean my email list?
Monthly for active senders (4+ campaigns/month). Quarterly minimum for everyone else. Always clean before major campaigns to your full list. Clean immediately after any campaign with bounce rates above 2%. For B2B lists, contact decay averages 25-30% annually—addresses go bad faster than most marketers expect.
What’s the difference between email delivery and email deliverability?
Delivery rate measures emails accepted by the receiving server (not bounced). Deliverability measures emails that reach the inbox (not spam). You can have 99% delivery and 70% deliverability—the server accepted your email, then routed it to spam. Deliverability is the metric that matters for campaign performance.
How do spam traps affect deliverability?
Spam traps are email addresses that exist only to catch senders with poor list practices. Hitting a pristine spam trap (never a real address) signals you’re using purchased or scraped lists—severe reputation damage. Hitting a recycled trap (abandoned address reactivated) signals you’re not maintaining list hygiene—moderate damage. One spam trap hit can drop deliverability 10-20% overnight.
Should I use a dedicated IP or shared IP?
Depends on volume. Under 50,000 emails/month: use shared IP—you won’t generate enough data to build dedicated IP reputation. Over 100,000/month: dedicated IP gives full control over your reputation. Between 50-100k: either works if you send consistently. Dedicated IPs require proper warmup; shared IPs depend on your ESP maintaining good pool reputation.
Why are my emails going to spam suddenly?
Common causes in order of likelihood: 1.Authentication failure (DNS change broke SPF/DKIM) 2.Blocklist addition (check MXToolbox immediately) 3.Spam complaint spike from recent campaign 4.Sending to old/unengaged segment triggered spam traps 5.Content triggered filters (new template, links, or offers) Check authentication first—it’s the most common cause and fastest to verify.
How do I check if my domain is blacklisted?
Use MXToolbox Blacklist Check or MultiRBL. Enter your sending domain and IP address. These tools check 50-100+ blocklists simultaneously. Check both domain and IP—they’re tracked separately. If listed, each blocklist page shows removal instructions.
Do engagement rates affect deliverability?
Yes, significantly. Mailbox providers track opens, clicks, replies, deletes, and complaints. High engagement signals your emails are wanted—more inbox placement. Low engagement signals your emails aren’t valued—more spam filtering. Gmail weights engagement heavily. Sending to unengaged subscribers drags down deliverability for your entire list.
How long does it take to improve email deliverability?
Minor issues (authentication fixes, list cleaning) show improvement within 1-2 weeks. Reputation recovery from serious damage takes 4-8 weeks minimum. Full recovery from blacklisting or major spam trap hits can take 3-6 months. Consistency matters more than speed—rushing the process by scaling too fast resets progress.
Can I recover from a blacklisted domain?
Yes, but it requires effort. First, identify why you were listed (spam traps, complaints, compromised sending). Fix the root cause completely. Then submit a delisting request to each blocklist—most have online forms. Some blocklists (Spamhaus, Barracuda) respond within 24-48 hours if your request is legitimate. Others take longer. If the underlying problem isn’t fixed, you’ll be relisted within days.
Does email size affect deliverability?
Indirectly. Emails over 100KB may load slowly or trigger soft bounces on recipients with full mailboxes. Image-heavy emails (large file sizes) often have poor text-to-image ratios, which triggers spam filters. Keep emails under 100KB total. Use hosted images instead of embedded ones. The content matters more than raw size.
How often should I clean my email list?
Monthly for active senders (4+ campaigns/month). Quarterly minimum for everyone else. Always clean before major campaigns to your full list. Clean immediately after any campaign with bounce rates above 2%. For B2B lists, contact decay averages 25-30% annually—addresses go bad faster than most marketers expect.
What’s the difference between email delivery and email deliverability?
Delivery rate measures emails accepted by the receiving server (not bounced). Deliverability measures emails that reach the inbox (not spam). You can have 99% delivery and 70% deliverability—the server accepted your email, then routed it to spam. Deliverability is the metric that matters for campaign performance.
How do spam traps affect deliverability?
Spam traps are email addresses that exist only to catch senders with poor list practices. Hitting a pristine spam trap (never a real address) signals you’re using purchased or scraped lists—severe reputation damage. Hitting a recycled trap (abandoned address reactivated) signals you’re not maintaining list hygiene—moderate damage. One spam trap hit can drop deliverability 10-20% overnight.
Should I use a dedicated IP or shared IP?
Depends on volume. Under 50,000 emails/month: use shared IP—you won’t generate enough data to build dedicated IP reputation. Over 100,000/month: dedicated IP gives full control over your reputation. Between 50-100k: either works if you send consistently. Dedicated IPs require proper warmup; shared IPs depend on your ESP maintaining good pool reputation.
Why are my emails going to spam suddenly?
Common causes in order of likelihood:
- Authentication failure (DNS change broke SPF/DKIM)
- Blocklist addition (check MXToolbox immediately)
- Spam complaint spike from recent campaign
- Sending to old/unengaged segment triggered spam traps
- Content triggered filters (new template, links, or offers)
Check authentication first—it’s the most common cause and fastest to verify.
How do I check if my domain is blacklisted?
Use MXToolbox Blacklist Check or MultiRBL. Enter your sending domain and IP address. These tools check 50-100+ blocklists simultaneously. Check both domain and IP—they’re tracked separately. If listed, each blocklist page shows removal instructions.
Do engagement rates affect deliverability?
Yes, significantly. Mailbox providers track opens, clicks, replies, deletes, and complaints. High engagement signals your emails are wanted—more inbox placement. Low engagement signals your emails aren’t valued—more spam filtering. Gmail weights engagement heavily. Sending to unengaged subscribers drags down deliverability for your entire list.